Data Analysis with SPSS
Preface
Statistical Package for the Social Science (SPSS)
Conducted by:
Kamarul Ariffin Mansor
Senior Lecturer
Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM)
Kedah Branch Campus
Malaysia
This module provides a comprehensive guide to conducting data analysis using SPSS, a widely used statistical software. It is structured into a step-by-step process that covers the entire workflow, from data preparation to advanced statistical tests. Key components include:
- Introduction: An overview of SPSS software and its role in statistical analysis. Data Inputs in SPSS Software: Instructions on importing and organizing data within SPSS, including file formats and data entry techniques.
- Data Transformation: Techniques to prepare data for analysis, such as recoding variables and computing new ones.
- Descriptive Statistics: Procedures for summarizing and describing data distributions, including measures of central tendency and dispersion.
- Test of Data Normality: Methods for assessing the normality of data using skewness and kurtosis.
- Test of Outliers: Identification and handling of outliers in both univariate and multivariate data sets.
- Test of Data Reliability: Evaluation of the internal consistency of scales using Cronbach’s Alpha.
- Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA): Techniques to uncover underlying structures in the data and reduce dimensionality.
- T-Tests: Application of one-sample, independent sample, and paired sample t-tests to compare means across groups or conditions.
- ANOVA Tests: Use of one-way, two-way, and repeated-measures ANOVA for analyzing variance among multiple groups.
- Correlation Tests: Examination of relationships between variables using correlation coefficients.
- Regression Analysis: Implementation of simple and multiple linear regression to model relationships between dependent and independent variables.
The module equips users with practical knowledge and step-by-step guidance to conduct data analysis in SPSS effectively, catering to both beginners and intermediate users. It emphasizes the integration of statistical theory with practical application, making it a valuable resource for researchers, students, and professionals in various fields.
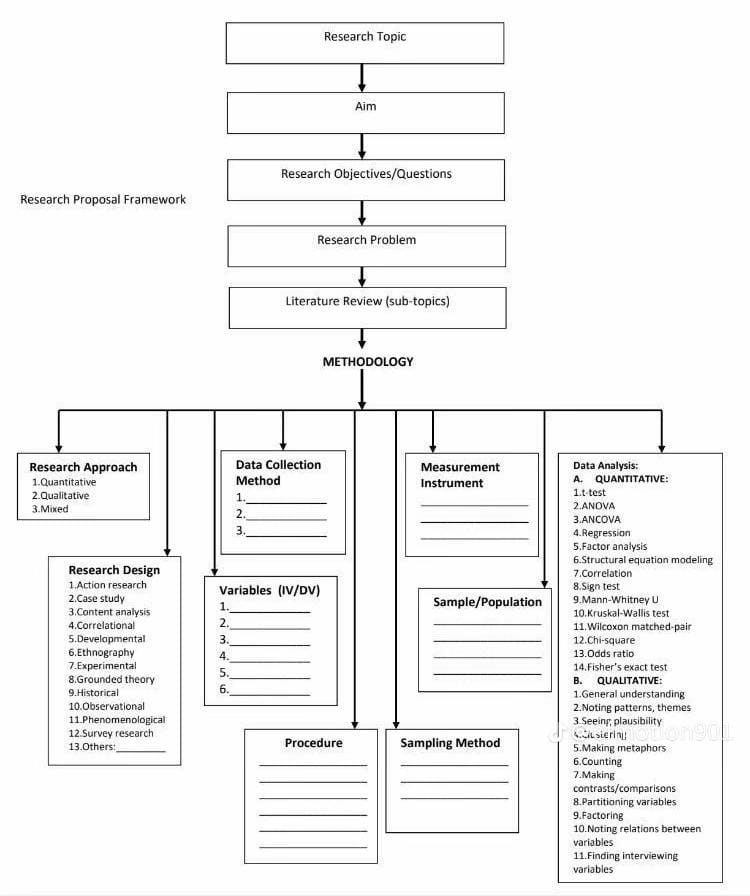
Research Framework
What is SPSS?
• Originally it is an acronym of Statistical Package for the Social Science but now it stands for Statistical Product and Service Solutions
• One of the most popular statistical packages which can perform highly complex data manipulation and analysis with simple instructions
SPSS Version
– The earlier versions of SPSS ran on mainframe computers
- SPSS 1 - 1968
- SPSS 2 - 1983
– SPSS/PC+ was first introduced in 1984
- SPSS 5 - 1993
– SPSS 6 for Windows was introduced in mid 1990’s
- SPSS 6.1 - 1995
- SPSS 7.5 - 1997
- SPSS 8 - 1998
- SPSS 9 - 1999
- SPSS 10 - 1999
- SPSS 11 - 2002
- SPSS 12 - 2004
- SPSS 13 - 2005
- SPSS 14 - 2006
– SPSS 15 - November 2006
– SPSS 16 - April 2008
– PASW Statistics 17 – December 2008
– PASW Statistics 18 – August 2009
– SPSS Statistics 19 – 2010
– SPSS Statistics 20 – 2011
– SPSS Statistics 21 – 2012
– SPSS Statistics 22 – 2013
– SPSS Statistics 23 – 2015
- SPSS 24 - 2016, March
- SPSS 25 - 2017, July
- SPSS 26 - 2018
- SPSS 27 - 2019, June (and 27.0.1 in November, 2020)
- SPSS 28 - 2021, May
- SPSS 29 - 2022, Sept
- SPSS 30 - 2024, Sept
SPSS is a software used for statistical analysis
First released in 1968 and was developed by Normane H. Bent and C. Hadial Hull
Since its release, SPSS was under SPSS Inc.
However in July 28, 2009 SPSS was acquired by IBM for US$1.2 billion
Versions 17 and 18 were known as PASW (Predictive and Analytical Software)
Version 19 was renamed as SPSS Statistics
Contents:
Step by Step Data Analysis Process by SPSS
- Introduction
- Data Inputs in SPSS Software
- Data Transformation
- Descriptive Statistics
- Test of Data Normality (skewness & kurtosis)
- Test of Outliers (univariate & multivariate)
- Test of Data Reliability (Cronbach’s Alpha)
- Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
- T-Tests (one sample, independent sample t-test, and paired sample t-test)
- ANOVA Tests (one-way, two-way, and repetitive measure ANOVA)
- Correlation Tests
- Regressions Analysis (Simple, and Multiple Linear Regression)
Download
data files
project information