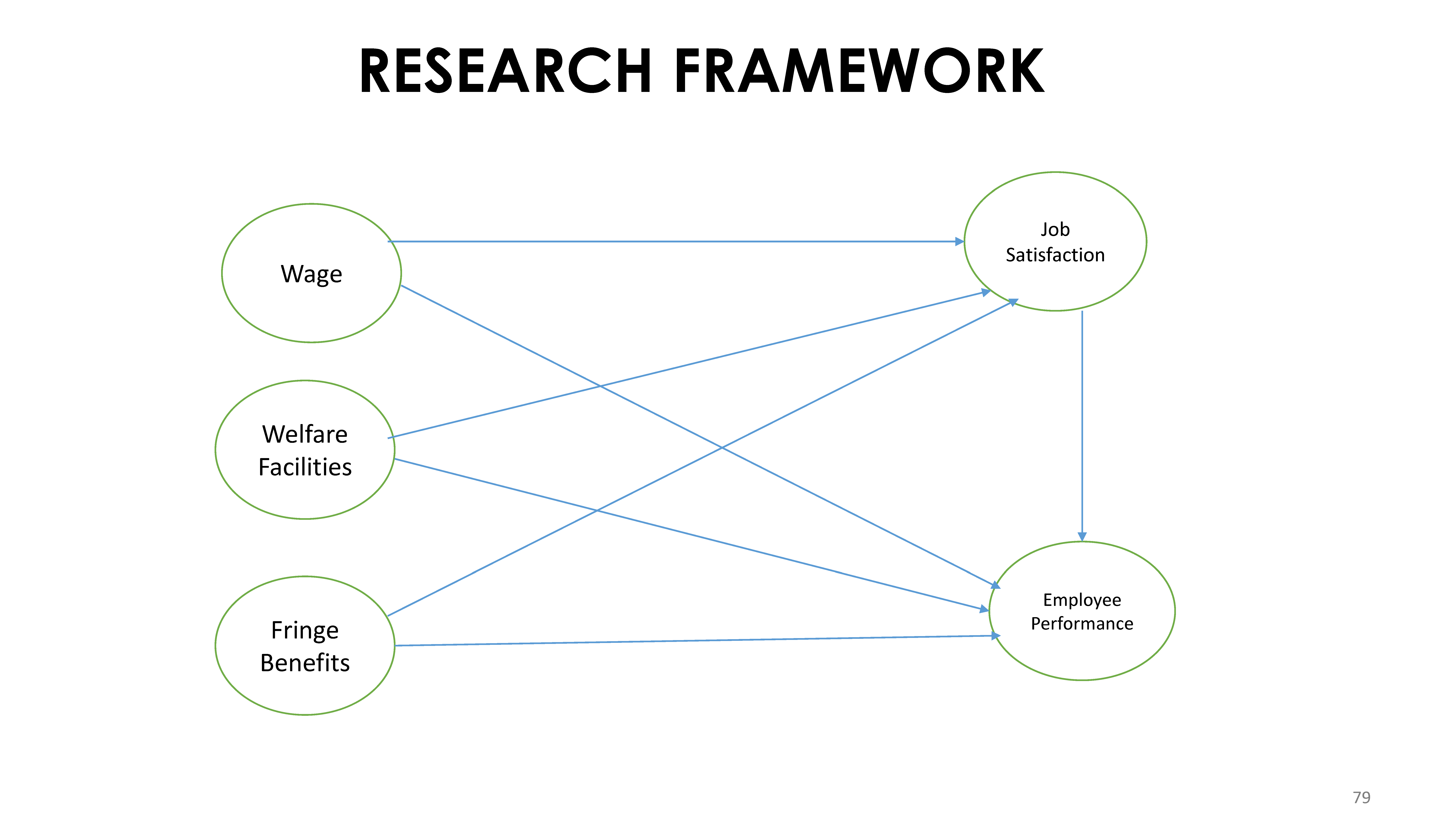
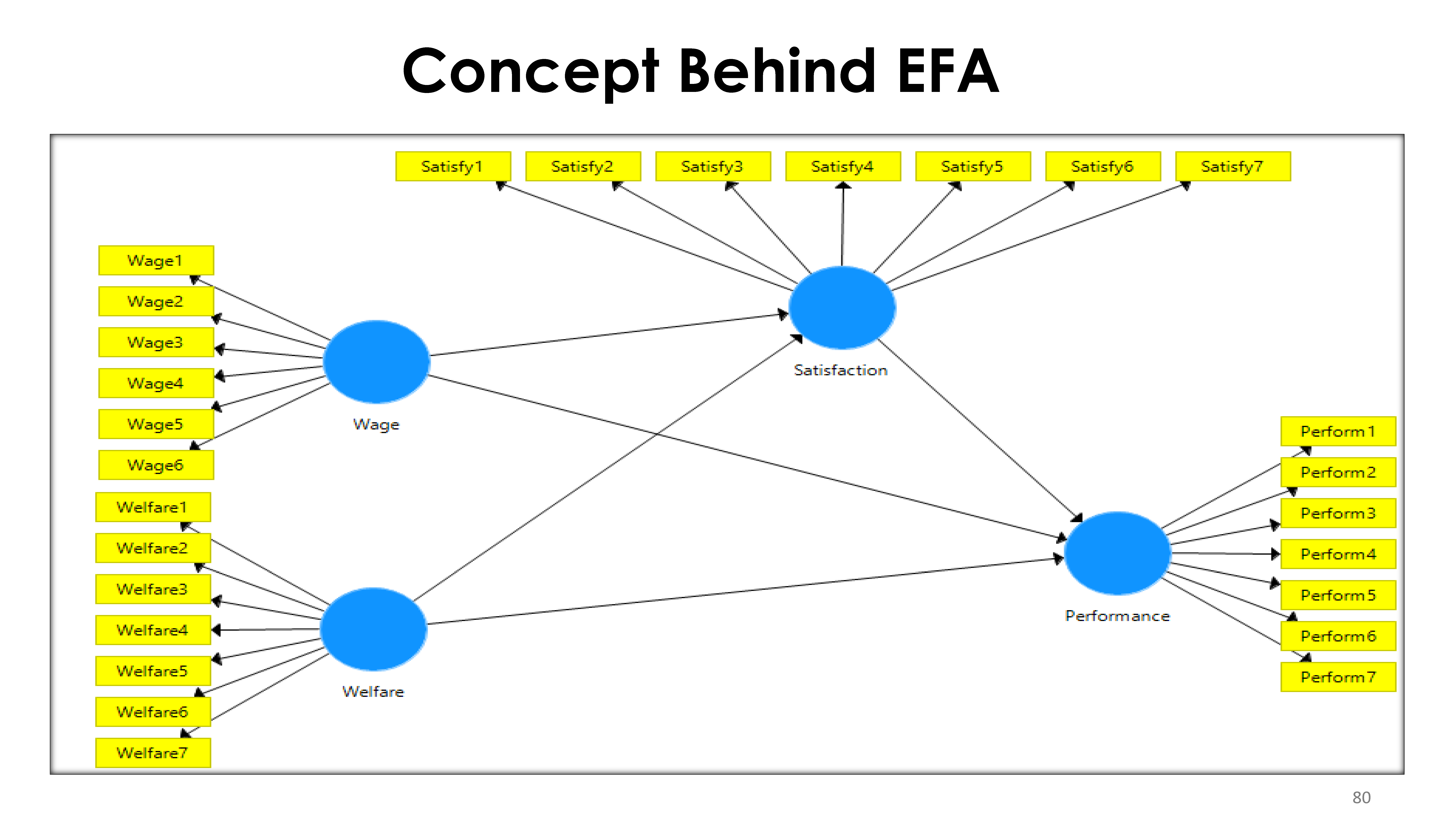
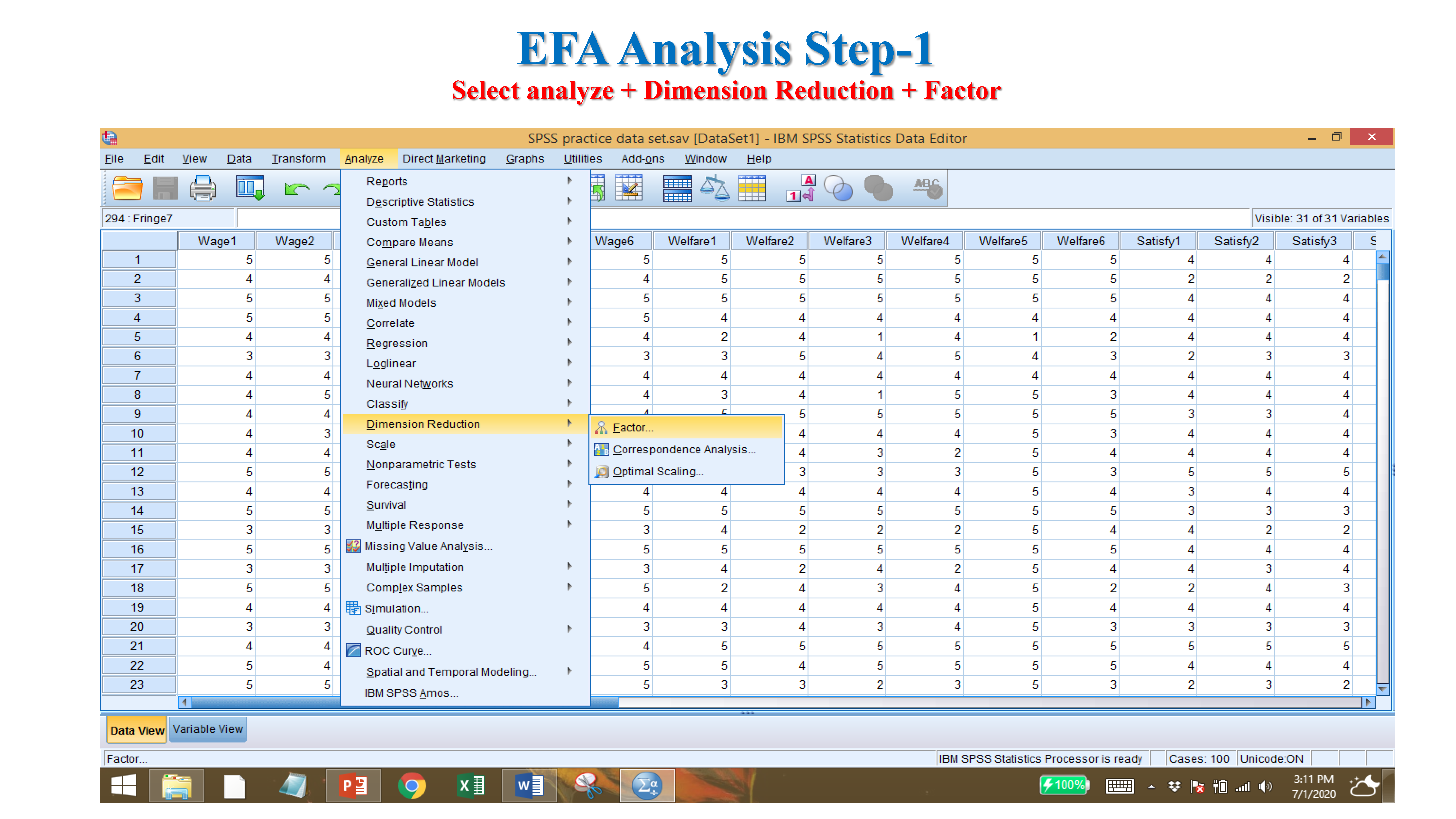
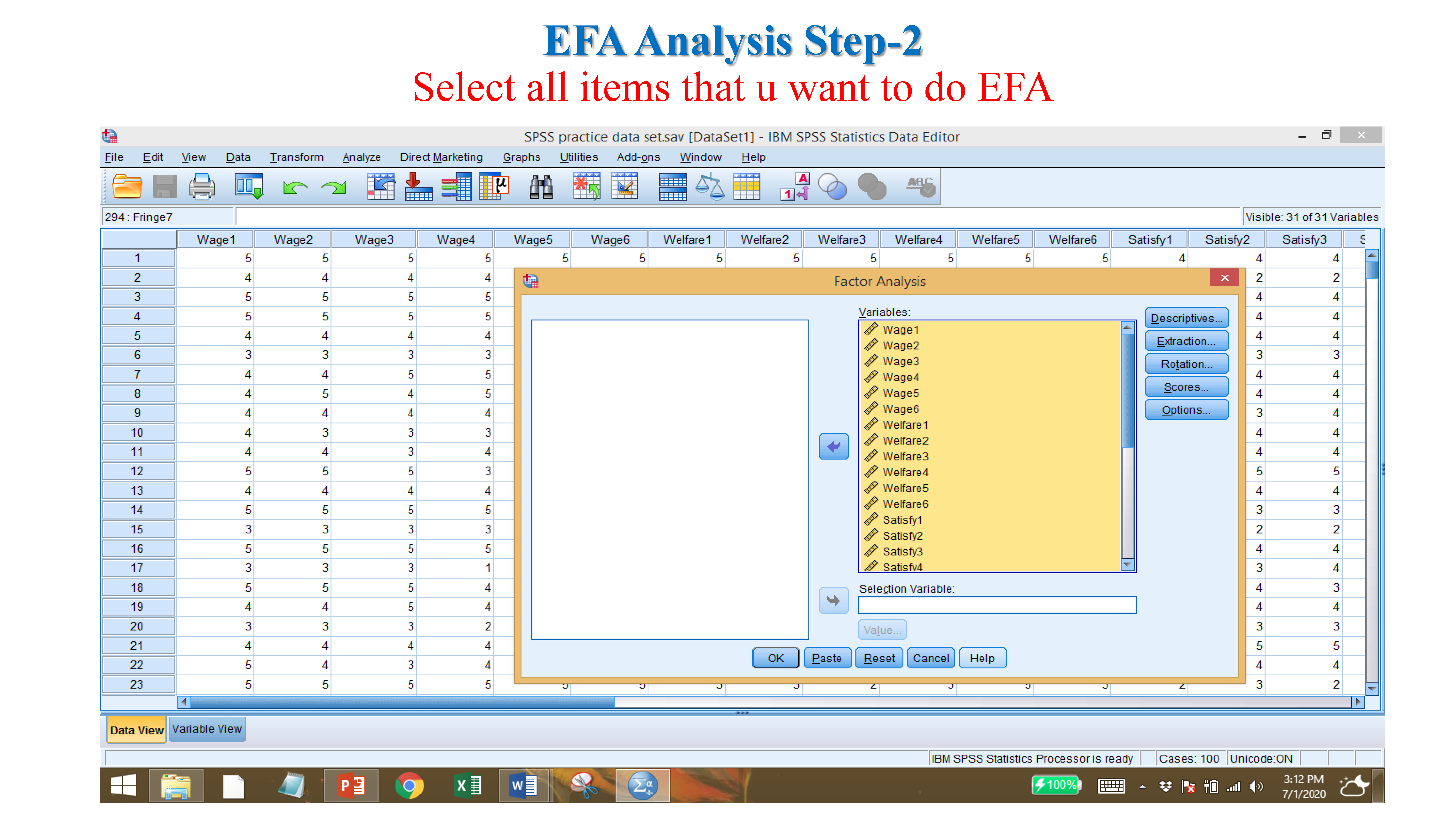
8 Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
In multivariate statistics, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) is a statistical method used to uncover the underlying structure of a relatively large set of variables. EFA is a technique within factor analysis whose overarching goal is to identify the underlying relationships between measured variables.
Assumption:
- Data must be Interval or Ratio measurement scale. E.g. Likert scale data or grouped data (1,2,3,4,5,6,7 point scale data).
- Sample size must at least 4/5 times of variables.
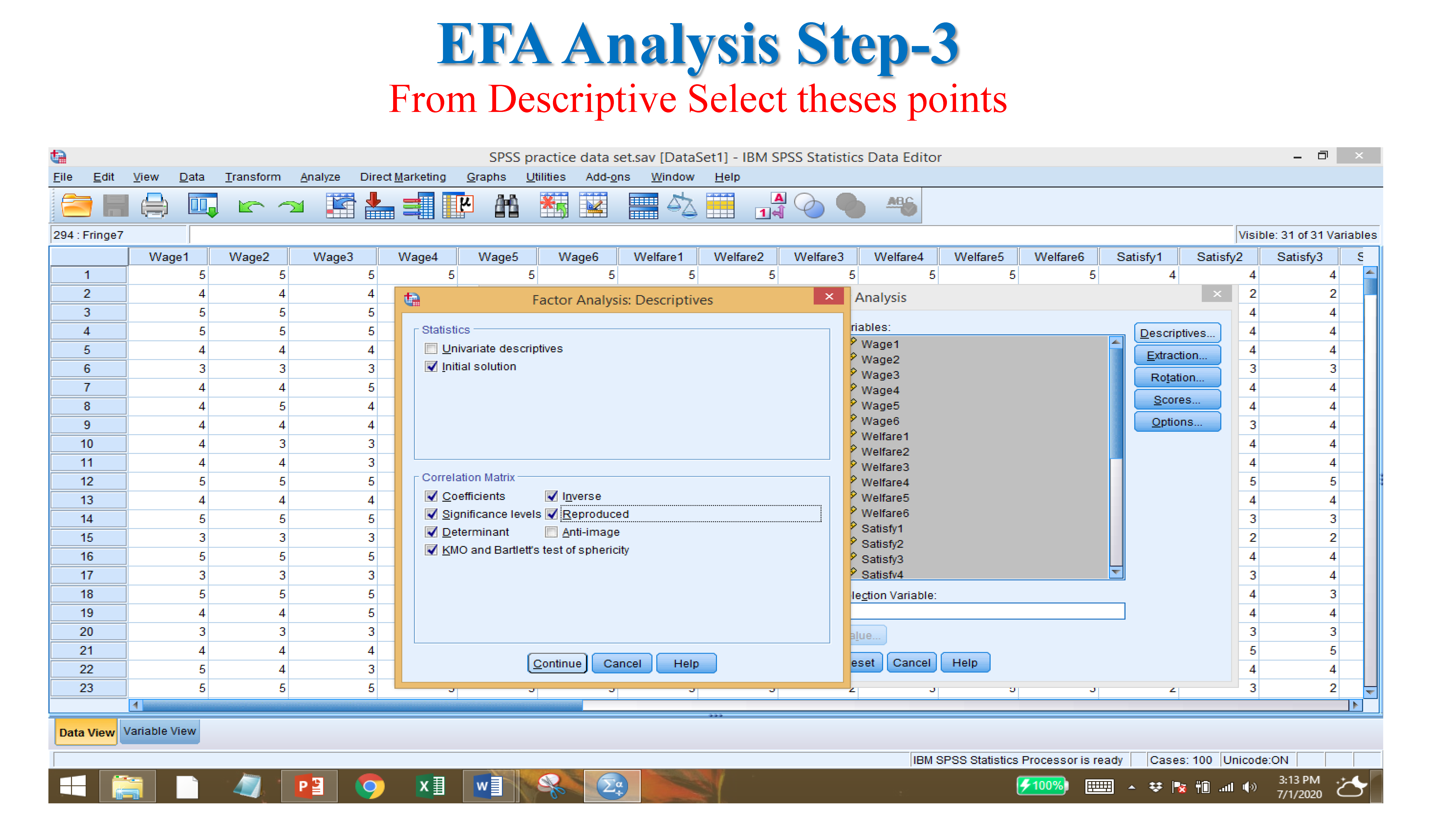
- Correlation Matrix: if values are near to +/- 1, and more than +.5 or -.5 these variable counts.
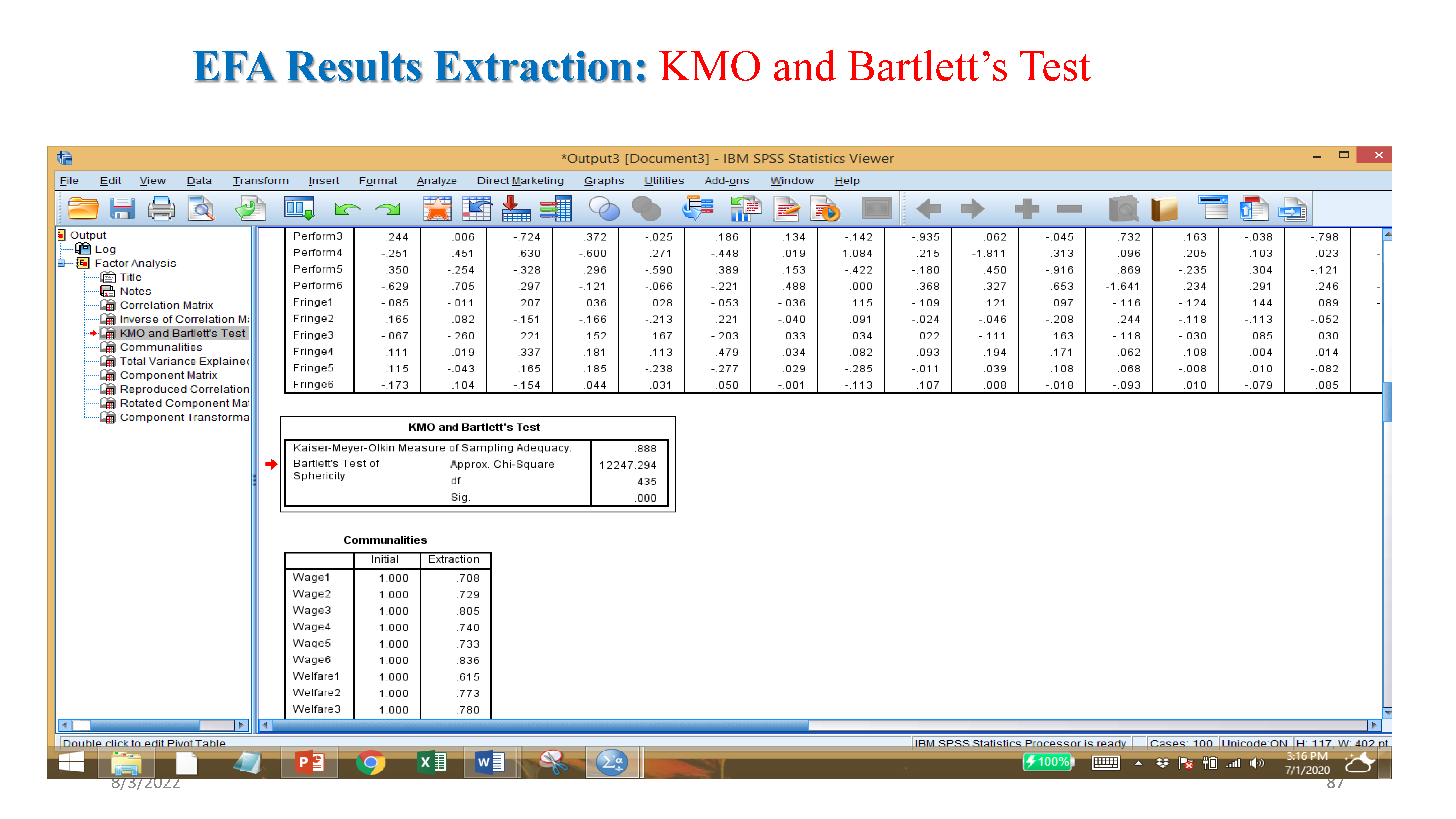
- KMO test: if value more than .5
- Bartlett’s test: if value sig. value smaller than .05 or .01.
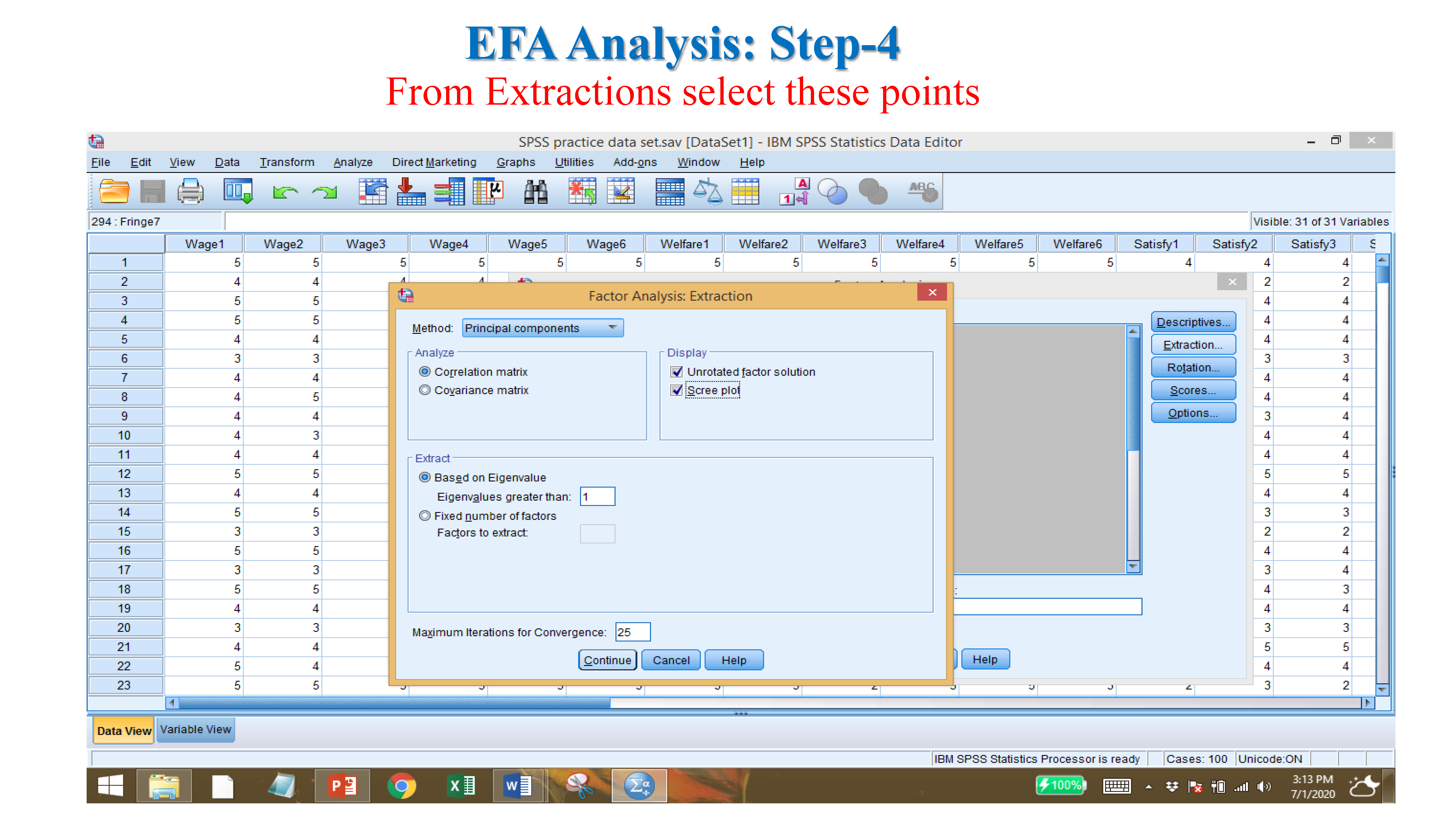
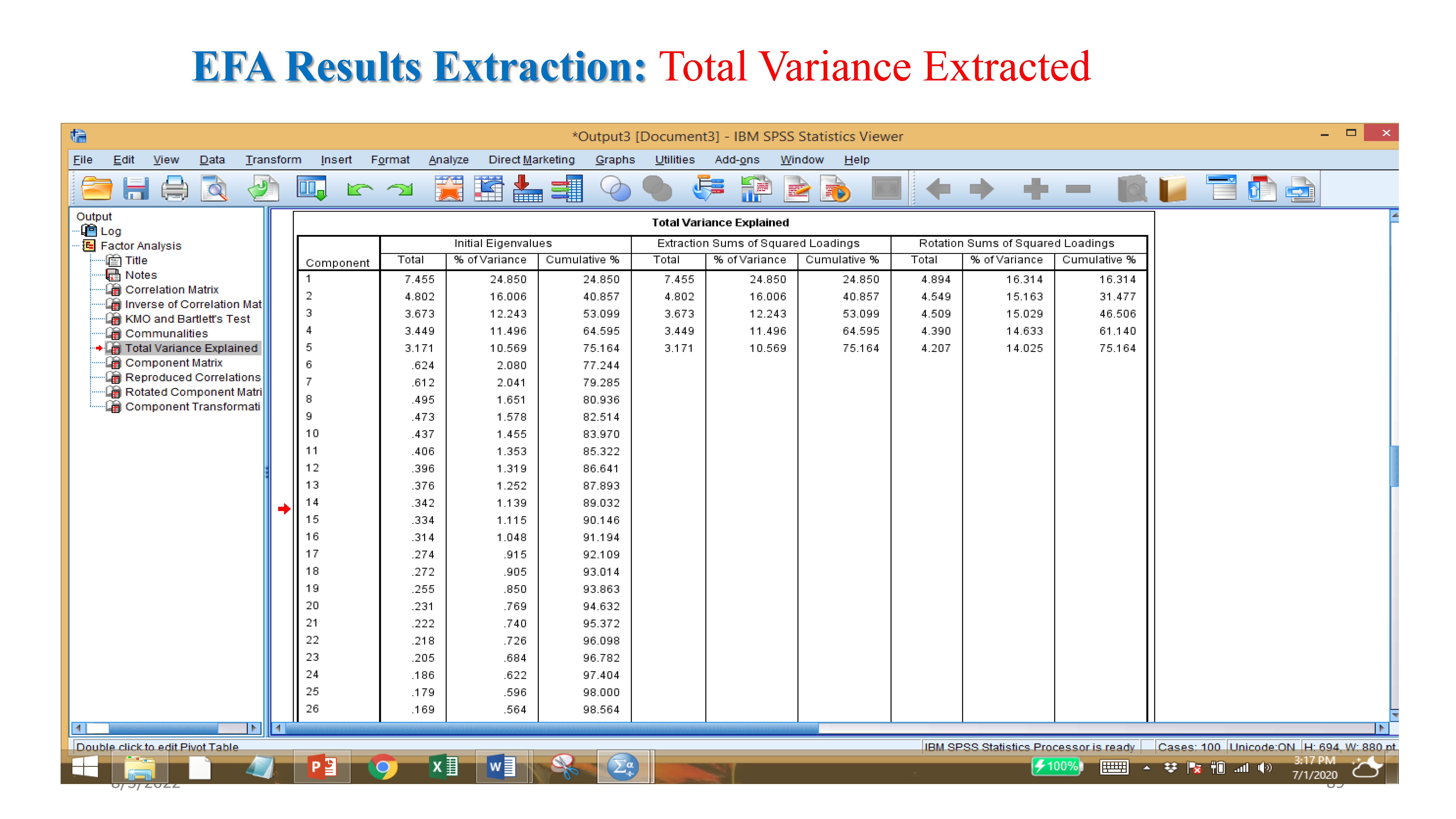
- Eigenvalues: components or variables having value 1 and more than 1.
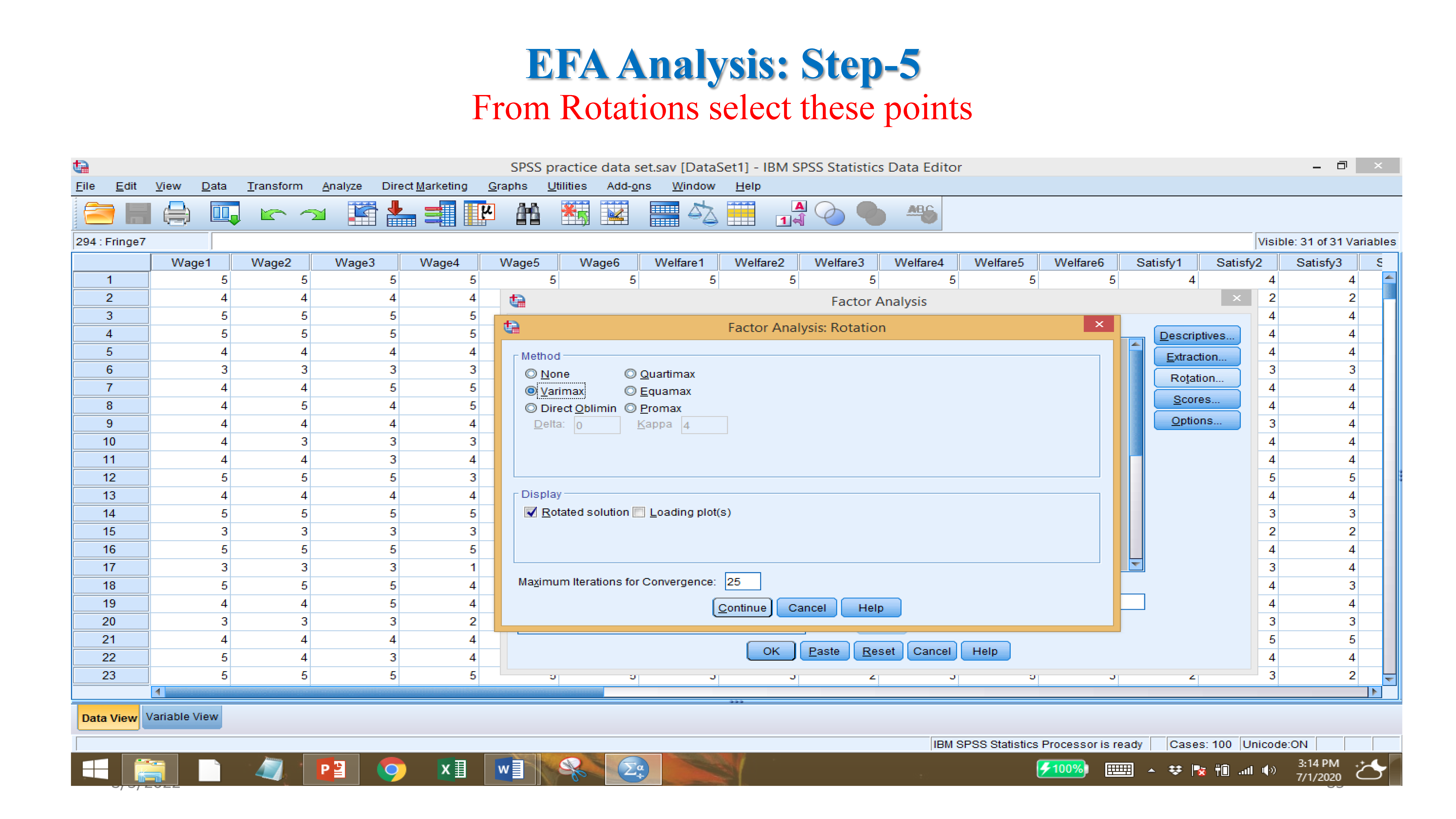
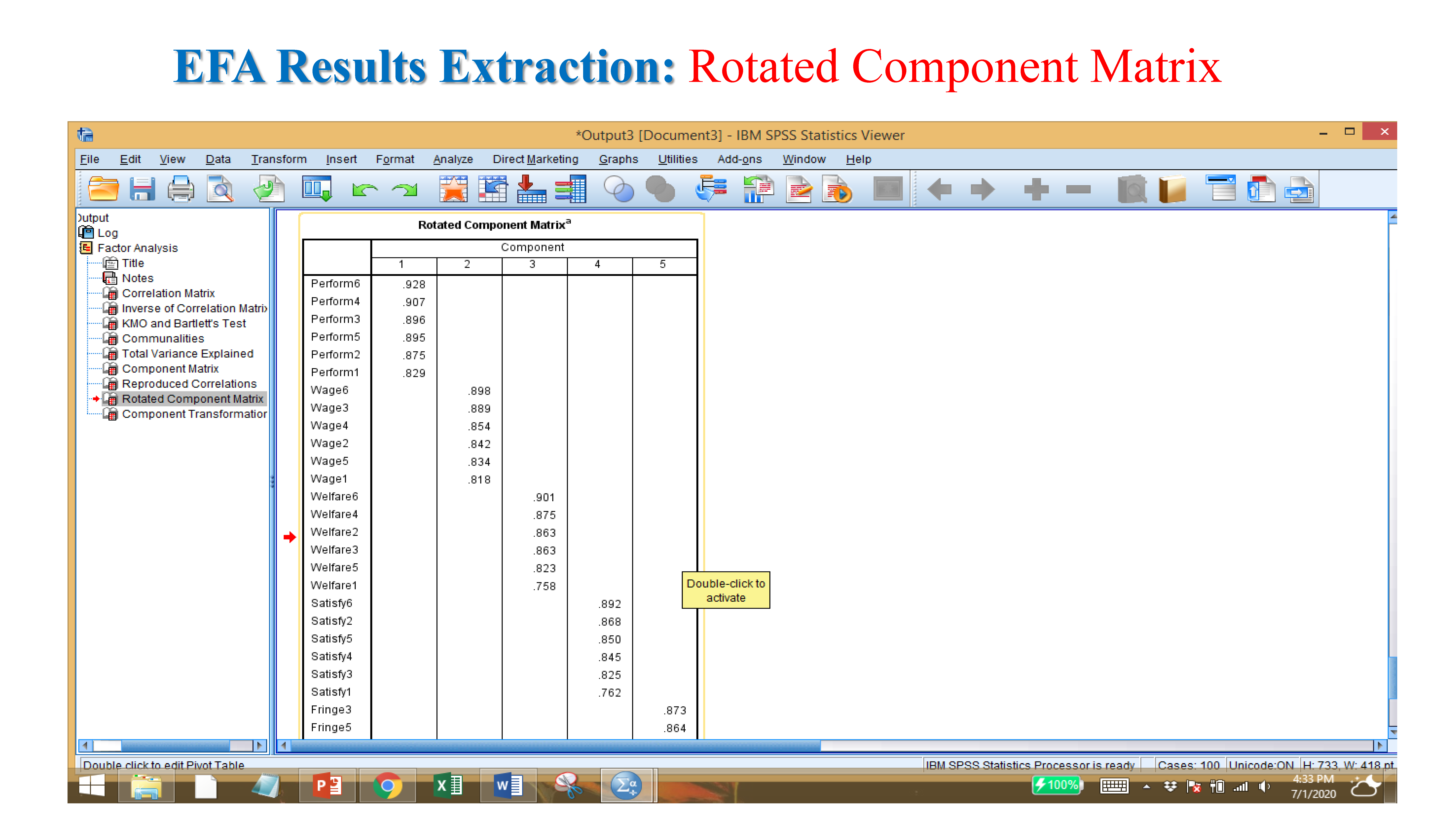
- Factor loading: if values exit in factors loading (item value more than .5).
- Multicollinearity: If in correlation matrix two items value is .80 or above, there is multicollinearity. Having same line, lying is the same lining.
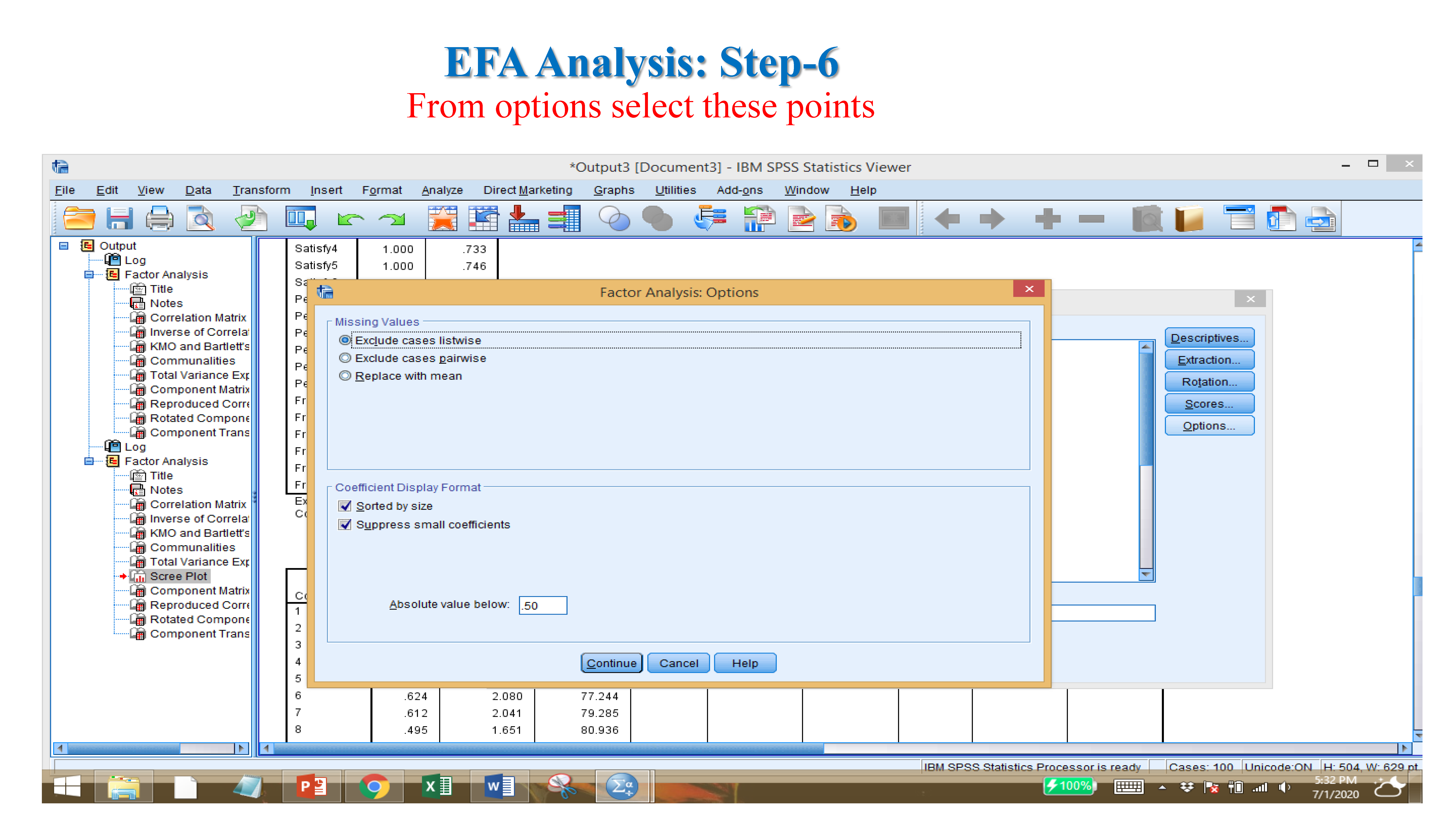
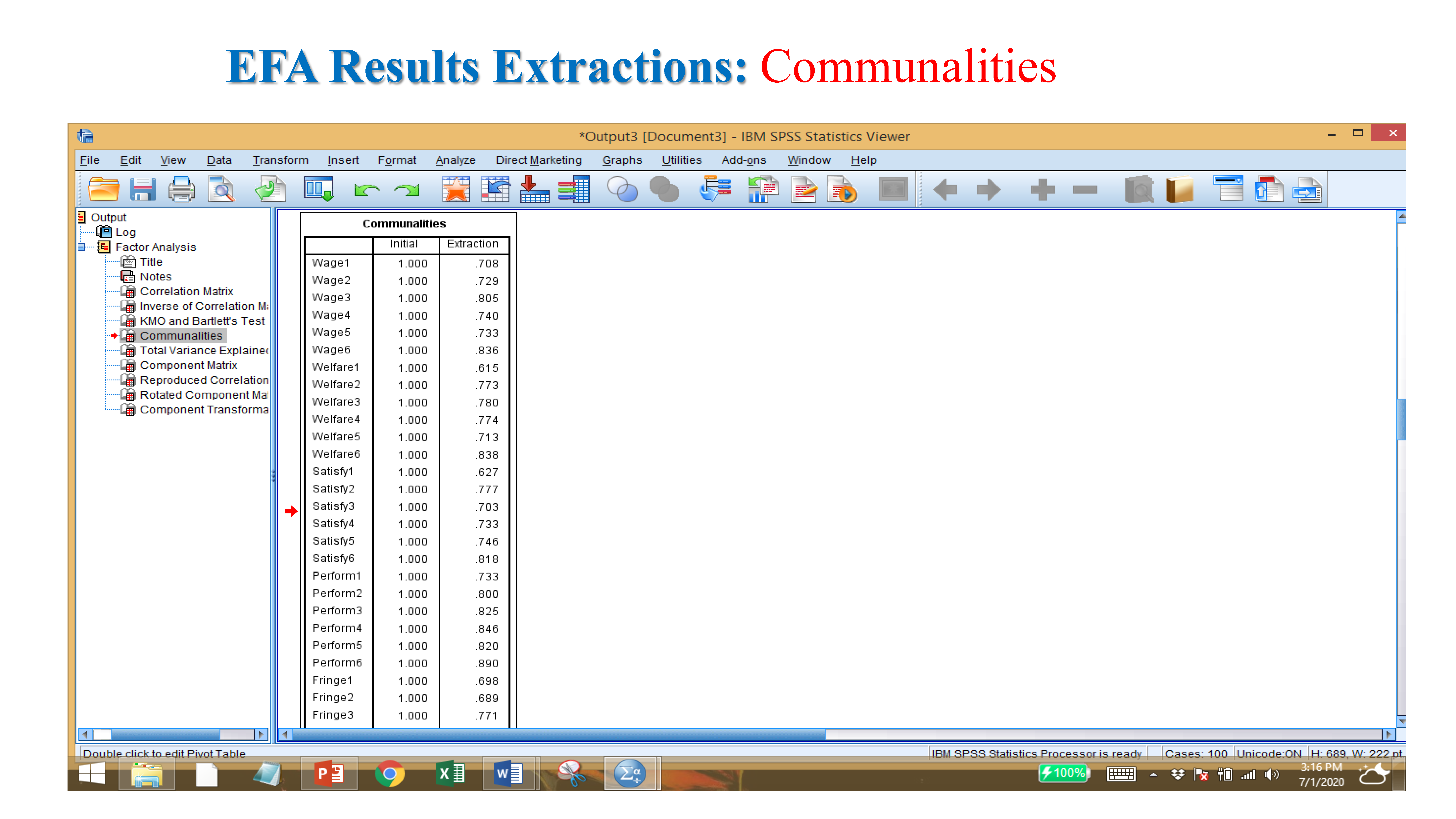
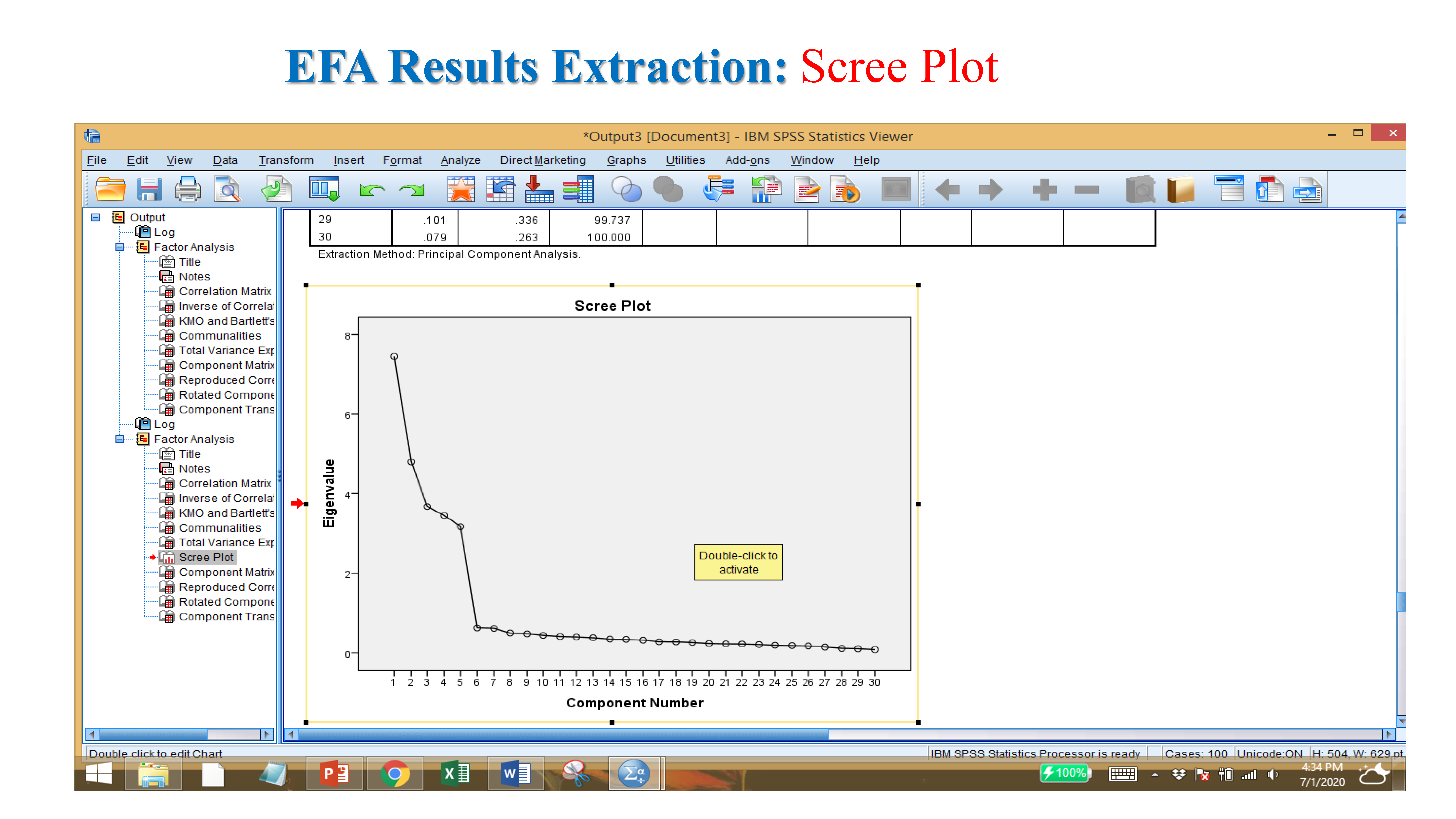
- Communality (component matrix): if value is near 1 or more than 70-80% (considered)- Scree plot: it show value more than 1.